
Normal resultsĮlectrical activity in the brain appears in an EEG as a pattern of waves. Your doctor may schedule an appointment to go over the test results with you. However, it does not always show past abnormalities related to a seizure.Ī neurologist (someone who specializes in nervous system disorders) interprets the recordings from the EEG and then sends the results to your doctor. The EEG may show abnormalities even if the seizure does not occur during the test. These EEGs use video to capture seizure activity. In some instances, a person may undergo a 24-hour EEG. They may ask you to lie still, close your eyes, breathe deeply, or look at stimuli (such as a flashing light or a picture).ĭuring the test, very little electricity passes between the electrodes and your skin, so you’ll feel very little to no discomfort. The technician may instruct you to do certain things while the test is in progress.This machine converts the electrical impulses into visual patterns that appear on a screen. Once the test begins, the electrodes send electrical impulse data from your brain to the recording machine.The technician will put a sticky gel adhesive on 16 to 25 electrodes and attach them to spots on your scalp.These spots are scrubbed with a special cream that helps the electrodes get a high-quality reading. A technician will measure your head and mark where to place the electrodes.You’ll lie down on your back in a reclining chair or on a bed.The test usually takes roughly 30 to 60 minutes to complete and involves the following steps: Specialized technicians administer EEGs at hospitals, doctor’s offices, and laboratories. The electrodes transfer information from your brain to a machine that measures and records the data. An electrode is a conductor through which an electric current enters or leaves. Other factors that can influence your EEG reading include:Īn EEG measures the electrical impulses in your brain by using several electrodes attached to your scalp. The person responsible for interpreting your EEG will take these movements into account. Several types of movements can potentially cause “artifacts” on an EEG recording that mimic brain waves. Factors that could interfere with an EEG reading Some people may not be able to hyperventilate safely, such as people with a history of stroke, asthma, or sickle cell anemia. Hyperventilation is also commonly induced during an EEG to produce abnormalities. The technician performing the EEG is trained to safely manage any situation that might occur. When someone has epilepsy or another seizure disorder, there’s a small risk that the stimuli presented during the test (such as a flashing light) may cause a seizure. If an EEG does not produce any abnormalities, stimuli such as strobe lights, or rapid breathing may be added to help induce any abnormalities.

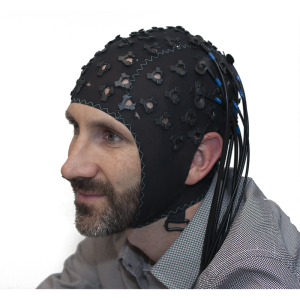
The number of patients excluded from the study will also be recorded, including the reason for exclusion.EEG is usually painless and very safe. Secondary assessment will also include interpretation of NCSE by a third independent reader if there is disagreement between first two. Secondary assessment will be qualified as acceptable or inacceptable interpretation based on whether greater or less than 50% of the recording is judged interpretable. Secondary quality assessment will be performed by two independent EEG interpreters blinded to clinical history. Initial diagnosis or exclusion of NCSE will be performed by on call resident, if the resident received prior training regarding EEG cap placement, and attending. The investigators will also record time to confirmation or exclusion of NCSE. The investigators will record time from neurology consultation request to placement of EEG cap as well as time from consultation request to obtaining a standard EEG. Prior to placement of EEG cap, evaluating staff member will request immediate standard-electrode EEG. This study will only be performed during times when EEG techs are not available onsite for rapid placement of standard 21-channel EEG electrodes, such as during night-call shifts. The placement of the EEG cap will be restricted to residents formally trained in its placement by an EEG tech. Why Should I Register and Submit Results?Īt the completion of neurology evaluation, if NCSE is in the differential diagnosis according to institution best practice, then consented participants will undergo placement of a large size, 20-channel EEG cap from Electro-Cap International with a Natus E-2-2520-26 electrode board adapter with initiation of recording.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
